Determination of traces of Cadmium and Lead in coal and rubberwood
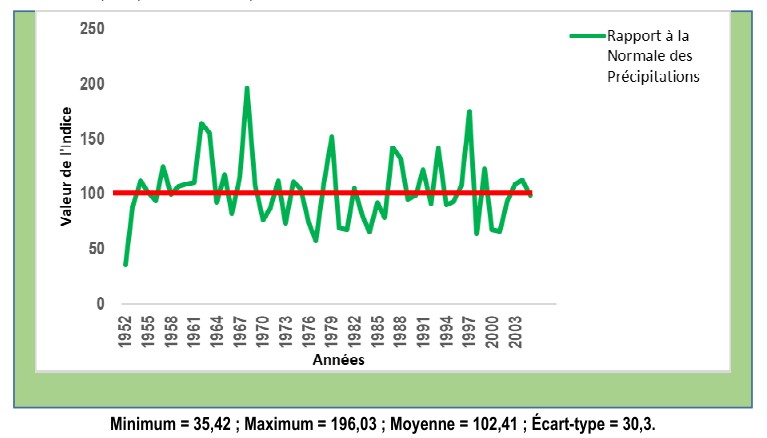
Look for lead and cadmium in charcoal and rubberwood before and after carbonization (pyrolysis) in order to assess their health quality. The charcoal was produced in a pyrolysis oven (between 800°C and 1000°) from fresh rubber wood and from dry rubber wood. Five samples including a sample of fresh wood, one of dry wood, a sample of latex as well as two samples of charcoal obtained by pyrolysis of fresh wood and dry wood. Results showed the presence of metallic trace elements (Cadmium and lead) in the analyzed samples. The lead content of fresh wood before carbonization increased from 0.506 mg/kg ± 0.238 to 1.526 mg/kg ± 0.258 after carbonization, a significant increase. The lead content of dry wood increased from 0.070 mg/kg ± 0.032 before carbonization to 0.797 mg/kg ± 0.025 after carbonization, a significant increase. Regarding cadmium, the content of fresh wood before carbonization went from 0.863 mg/kg ± 0.075 to 0.201 mg/kg ± 0.042 after carbonization, a significant drop. The cadmium content of dry wood increased from 0.801 mg/kg ± 0.112 before carbonization to 0.241 mg/kg ± 0.012 after carbonization, a significant drop. The presence of trace metals elements in charcoal and rubberwood makes its use as fuel wood unsuitable for the culinary process and grilling.
Copyright (c) 2025 Bulletin de la Recherche Agronomique du Bénin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Les articles publiés par le Bulletin de la Recherche Agronomique du Bénin sont en libre accès. Ils sont gratuits pour tout le monde, immédiatement téléchargeables dès la publication et distribués sous la licence CC BY-NC-ND (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).