Plant biodiversity conservation determinants in the West Africa dry woodlands
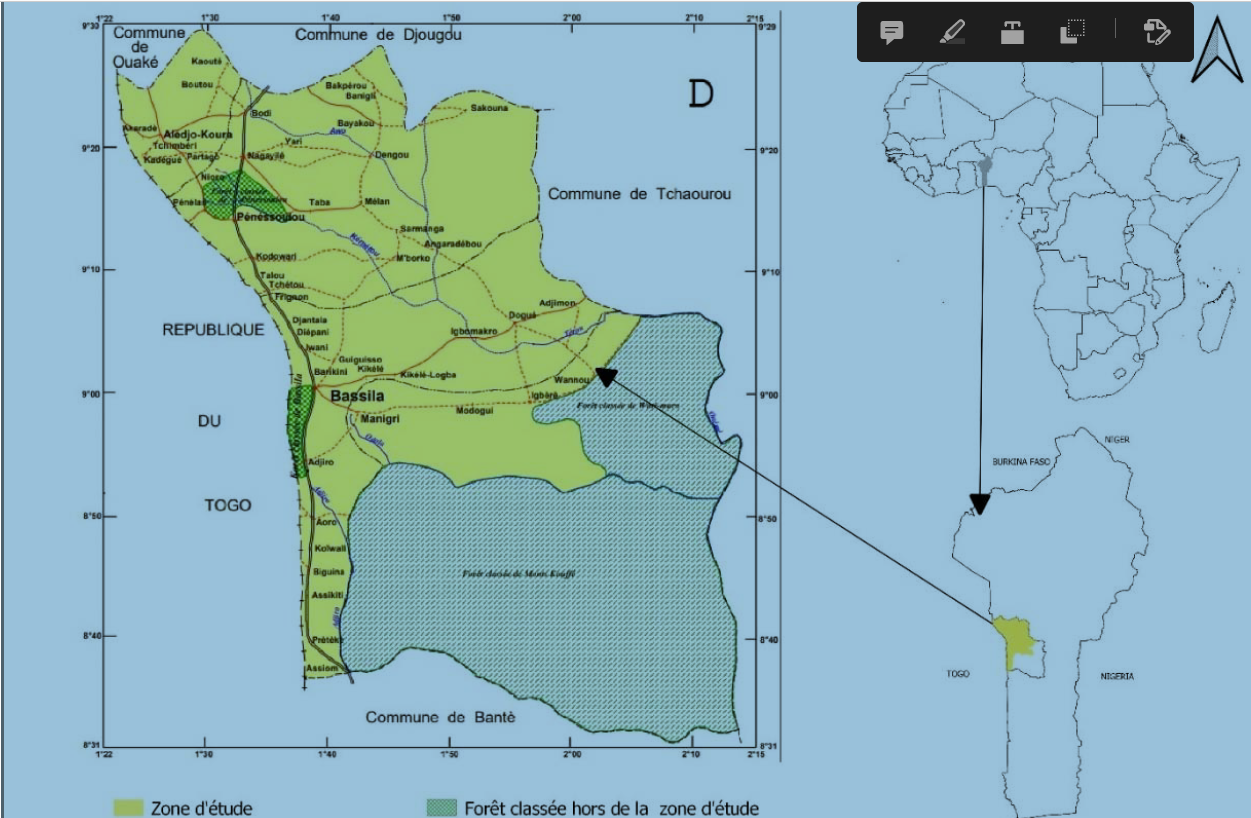
The study consisted of identifying, using spatial remote sensing, plant biodiversity conservation determinants of the West Africa woodlands in the management forests context. The linear model was used to determine, in the Bassila Forest Resources Restoration Project (PRRF) intervention zone, the effect of the mode of ownership, the size and location of the plant cover, as well as the effect of the period (during or after the project) on the evolution of land use classes coverage rate. The results
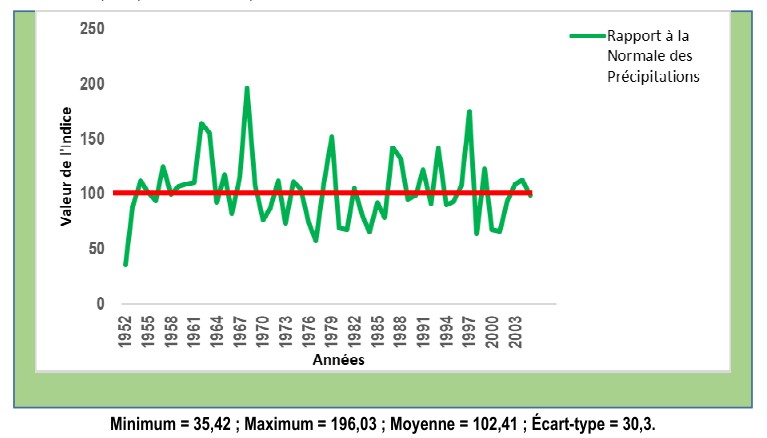
showed that the coverage rate of forests and savannahs decreased significantly in the post-project period (respectively F = 17.75 ; p = 0.000123 and F = 9.801 ; p = 0.003095). The type of ownership, the size of the vegetation cover and its location had no significant effect on forest conservation. Therefore the period (during and after the project) is designed as determining the conservation of forest biodiversity in the PRRF intervention area. However, other factors such as the high cost and complexity of planned activities for the local managers, the climate, the phytogeography and the urbanization can also impact the biodiversity conservation of dry tropical forests. Thus the study must be extended to take into account the factors (cost and complexity of planned activities for the local managers, climate, phytogeography, urbanization, etc.) for the forest biodiversity conservation in a dry tropical environment.
Les articles publiés par le Bulletin de la Recherche Agronomique du Bénin sont en libre accès. Ils sont gratuits pour tout le monde, immédiatement téléchargeables dès la publication et distribués sous la licence CC BY-NC-ND (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).