Gender-sensitive analysis of farmers' willingness to pay for an agricultural insurance service in areas vulnerable to climate change
Downloads
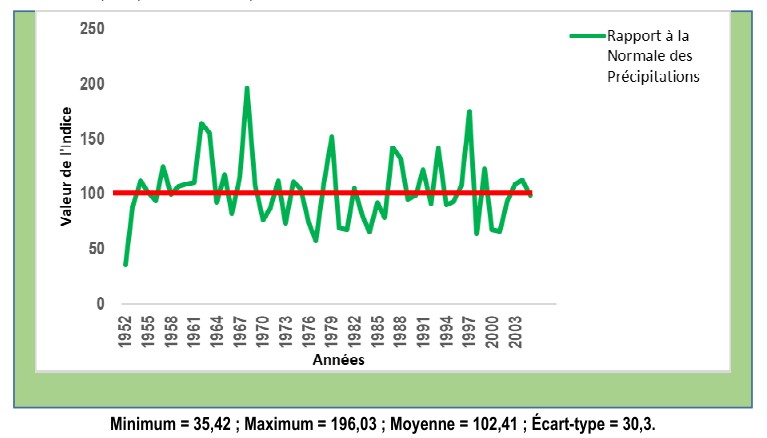
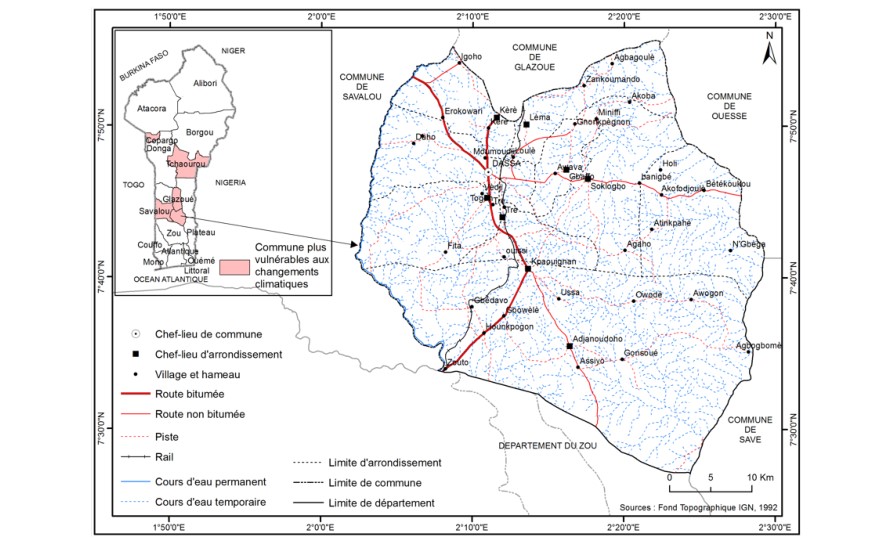
Willingness to pay is an essential concept in agriculture, referring to farmers' willingness to pay a sum of money for the acquisition of a good or service. The double objective of the study was to analyse -i- farmers' preferences in terms of the crops they choose to insure and -ii- the determinants of their willingness to pay for an insurance service in Dassa-Zoumé, a commune in central Benin that is highly vulnerable to climate change. Data were collected using a structured questionnaire from 318 randomly selected households in ten districts. Crop preferences were analysed using descriptive statistics. To identify the determinants of willingness to pay, a multiple linear regression model was estimated using R statistical software. The results showed that farmers had a preference for soya and maize two crops to be insured. The variables gender, membership of a professional agricultural organization and type of farmer had a positive influence on farmers' willingness to pay. Commercial farmers had been willing to pay a significantly (p ˂ 0.05) higher amount for soya bean cultivation (5,094 FCFA) than subsistence farmers (2,800 FCFA). On the other hand, for the same crop, women were prepared to pay an average premium of 3,854 FCFA, while men were prepared to pay a premium of 6,108 FCFA. In the light of these results, insurance companies need to take account of beneficiaries' preferences in terms of the crops to be insured and the purchasing power of the different target groups in order to reduce the risk of agricultural insurance failure.